Ever heard someone throw around terms like “tort” and “personal injury lawsuit” and wondered if they were the same thing? You’re not alone! The legal world can feel like its own language, and understanding the nuances between similar concepts is crucial, especially if you’re ever involved in a legal situation. This guide will break down the key differences between a tort and a personal injury lawsuit, explaining how they affect you and what you need to know.
Difference Between a Tort and a Personal Injury Lawsuit
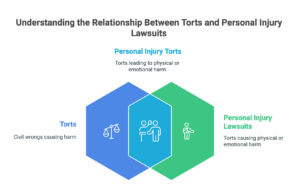
Think of “tort” as the category, and “personal injury” as one type of item in that category. A tort is simply a civil wrong that causes someone else to suffer harm or loss, resulting in legal liability for the person who committed the act. This harm can be physical, emotional, or even financial.
A personal injury lawsuit is a specific type of lawsuit alleging a tort that resulted in physical or emotional harm to a person. In other words, all personal injury lawsuits are torts, but not all torts are personal injury lawsuits. Got it? Let’s dig deeper.
Negligence Tort Examples: Understanding the Foundation of Many Personal Injury Lawsuits
Many personal injury cases are built on the legal concept of negligence. Negligence occurs when someone fails to exercise a reasonable standard of care, resulting in harm to another person.
Here are a few examples:
- Car Accidents: A driver speeding through a red light and colliding with another vehicle. This is one of the most common causes of personal injury lawsuits.
- Slip and Fall: A store owner fails to clean up a spilt liquid, causing a customer to slip, fall, and break a bone.
- Medical Malpractice: A doctor prescribing the wrong medication to a patient, leading to adverse health effects. According to a 2022 study by the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB), over 13,000 medical malpractice payment reports were filed in the United States.
Beyond negligence, other torts can lead to personal injury lawsuits, such as intentional torts like assault and battery.
Lawsuit Lingo: Why Knowing the Difference Matters to You
Why should you care about this legal jargon? Understanding the difference between a tort and a personal injury lawsuit can significantly impact your rights and options.
- Knowing your options: If you’ve been wronged, understanding the type of tort involved helps you determine the best course of action. Is it a personal injury case, or something else?
- Building a strong case: Identifying the correct legal basis for your claim (e.g., negligence, nuisance, defamation) is crucial for building a strong and successful case.
- Understanding potential damages: Different types of torts may allow for different kinds of damages (financial compensation).
What is a Tort Claim and How Does it Lead to a Personal Injury Case?
A tort claim is a formal assertion that someone has committed a tort and is therefore liable for the resulting damages. It’s the initial step in seeking compensation for harm caused. If the tort results in physical or emotional injury, the tort claim may evolve into a personal injury case.
For example, imagine your neighbour is constantly playing loud music at 3 AM. This could be considered the tort of nuisance, which is interfering with your enjoyment of your property. You could file a tort claim against them. If you suffer stress-induced insomnia as a result, you might even consider that personal injury, but the core tort is the nuisance.
7 Key Differences that Can Make or Break Your Case
Here are seven crucial differences between a tort and a personal injury lawsuit:
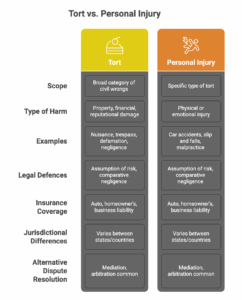
- Scope: A tort is a broad category encompassing many civil wrongs. Personal injury is a specific type of tort involving physical or emotional harm.
- Type of Harm: Tort claims can involve property damage, financial loss, or reputational damage. Personal injury lawsuits always involve physical or emotional injury.
- Examples: Tort examples include: nuisance (noisy neighbour), trespass to land (walking on someone’s property without permission), defamation (harming someone’s reputation through false statements), and negligence (careless actions). Personal injury examples include: car accidents, slip and falls, and medical malpractice.
- Legal Defences: While some defences like assumption of risk and comparative negligence apply broadly across tort law, their applicability can vary depending on the specific tort involved. For example, the defence of “consent” might be relevant in a battery case (an intentional tort), but not in a negligence case.
- Insurance Coverage: Many tort claims, especially personal injury claims, are handled through insurance. Car accidents often involve auto insurance, while slip and fall cases might include homeowner’s or business liability insurance. The specific type of insurance policy and its terms play a significant role in the handling of the claim.
- Jurisdictional Differences: Tort law and personal injury law can vary significantly between states or even countries. For example, some states have stricter rules regarding medical malpractice claims than others. The statute of limitations (the deadline for filing a lawsuit) also varies.
- Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): While lawsuits are a common way to resolve tort claims, many cases are settled through ADR methods like mediation or arbitration. Mediation involves a neutral third party helping the parties reach a settlement agreement, while arbitration involves a neutral third party making a binding decision. ADR can often be a faster and less expensive way to resolve a tort claim than going to court.
When to File a Tort Claim vs. a Personal Injury Lawsuit
Generally, you’ll start with a tort claim. If that tort resulted in physical or emotional injury, you might then escalate it into a personal injury lawsuit. You’ll want to file a claim as soon as you realise you’ve been harmed, and you should consult with an attorney. If you are unsure what steps to take, a legal professional will assess the circumstances and guide you toward the most appropriate action, whether it’s a simple tort claim or a more complex personal injury lawsuit. Seeking legal guidance ensures your rights are protected and your case is presented effectively.



It is actually a great and helpful piece of information. I’m satisfied that you simply shared this useful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.