Being injured at work can feel overwhelming. Not only are you dealing with physical pain and recovery, but you might also face unexpected challenges from your employer. This guide offers practical advice on protecting your rights and getting the support you deserve.
1. Understanding Your Rights as an Injured Worker
UK law protects employees injured at work. The key piece of legislation is the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974. This, alongside related regulations, ensures employers must provide a safe working environment. If they fail, and you’re injured as a result, you have rights.
Your rights include:
- Reporting the injury without fear of reprisal.
- Accessing appropriate medical care.
- Receiving workers’ compensation benefits to cover lost wages and medical expenses.
- Returning to work safely, potentially with modified duties.
- Fair treatment throughout the entire process.
Knowing these rights is your first line of defence.
2. Reporting Your Injury: A Critical First Step with Your Employer
Report your injury immediately. Don’t delay, even if you think it’s minor. Inform your supervisor and follow your company’s reporting procedures. This usually involves completing an accident report form.
The report should include:
- Date, time, and location of the incident.
- A detailed description of how the injury occurred.
- The specific body parts affected.
- Names of any witnesses.
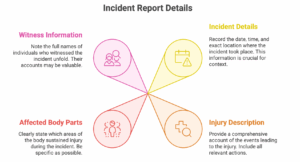
Keep a copy of the report for your records. Reporting promptly begins the workers’ compensation claim process and creates a vital written record. Remember, under the Reporting of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations 2013 (RIDDOR), your employer also has legal obligations to report specific serious workplace incidents to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE).
3. Documenting Everything: Building a Strong Case
Detailed documentation is vital. Keep records of everything related to your injury, including:
- Accident reports.
- Medical records (doctor’s notes, test results, treatment plans).
- Correspondence with your employer, insurance company, and medical professionals.
- Photos or videos of the accident scene (if possible).
- A daily journal detailing your pain levels, limitations, and impact on your daily life.
This documentation becomes your evidence if disputes arise.
4. Medical Care and Treatment: Ensuring You Get What You Need
Seek immediate medical attention. Follow your doctor’s treatment plan diligently. Don’t skip appointments or deviate from prescribed medications.
In the UK, your employer’s insurer will usually have a preferred network of medical professionals. Whilst you might have a degree of choice, understand their processes and potential limitations. If you have concerns about the treatment you are receiving, discuss this with your doctor and consider seeking a second opinion.
5. Dealing with Employer Pushback: Strategies for Protection
Some employers, unfortunately, create obstacles for injured workers. They might question the validity of your injury, pressure you to return to work too soon, or deny your claim.
If you encounter such pushback:
- Stay calm and professional.
- Document all interactions (dates, times, who you spoke with, and what was said).
- Know your rights. Refer back to the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 and related regulations.
- Seek support from your union representative, if applicable.
- Don’t sign anything without understanding its implications and seeking legal advice.
A 2023 study by the HSE showed that disagreements regarding return-to-work plans are a common cause of disputes between employers and injured workers. Having a clear, documented plan approved by your doctor is crucial.
6. Financial Security: Navigating Lost Wages and Benefits After Injury
Workers’ compensation benefits aim to cover lost wages and medical expenses. In the UK, these benefits are usually paid through your employer’s insurance.
The amount of compensation you receive depends on several factors, including your average weekly earnings and the severity of your injury. Understand how your benefits are calculated and ensure you receive the correct amount promptly. If payments are delayed or denied, seek legal advice.
Remember that employer insurance premiums are affected by workplace incidents, so some employers may be reluctant to act immediately. However, this should not affect your legal right to compensation.
7. Seeking Legal Counsel: When to Fight Back Against Your Employer
Consider seeking legal counsel if:
- Your workers’ compensation claim is denied.
- Your employer is pressuring you to return to work prematurely.
- You are experiencing discrimination or retaliation.
- Your injury is severe, and you anticipate long-term medical needs.
A solicitor specialising in workplace injuries can assess your case, advise you on your legal options, and represent you in negotiations or legal proceedings. For example, if there’s a dispute regarding the recommended treatment plan or return-to-work accommodations, legal assistance can prove invaluable. Many solicitors offer free initial consultations.
Facing an injury at work is difficult, but understanding your rights and taking proactive steps can make the process much smoother. By documenting everything, seeking appropriate medical care, and knowing when to seek legal help, you can protect yourself and ensure a fair outcome.





You made some respectable factors there. I regarded on the internet for the issue and located most individuals will associate with along with your website.