Losing a loved one is devastating. When that loss is caused by someone else’s carelessness, the grief is often compounded by anger and a desire for justice. A “wrongful death” occurs when someone dies due to the negligence, recklessness, or intentional act of another person or entity. This article explains wrongful death claims and how to hold negligent parties responsible.
Understanding Wrongful Death: Definition and Legal Basis
A wrongful death claim is a civil lawsuit filed by the surviving family members of a deceased person against the party responsible for their death. These claims aren’t about criminal punishment; they’re about seeking financial compensation for the losses suffered because of the death. The legal basis for these claims lies in state statutes, which vary significantly. For instance, some states, like California, have very broad definitions of who can file a claim, while others, such as Massachusetts, are more restrictive.
What Constitutes a Wrongful Death Claim?
A successful wrongful death claim generally needs to prove several key elements:
- Death: The obvious starting point is establishing that a death occurred.
- Negligence or Wrongful Act: You need to show that the death was caused by someone else’s negligence, recklessness, or intentional act. Negligence means that the person or entity had a duty of care, breached that duty, and this breach directly caused the death. Examples of negligence range from a distracted driver causing a car accident to a doctor making a fatal error during surgery.
- Damages: The death must have resulted in financial damages to the surviving family members. These damages can include lost income, medical expenses, funeral costs, and loss of companionship.
- Survival Action: Some states also allow for a “survival action,” which allows the estate to recover damages the deceased suffered between the injury and death, such as pain and suffering.
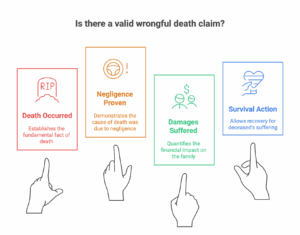
The degree of negligence can also impact the outcome. Gross negligence, a higher level of carelessness involving a conscious disregard for safety, or even recklessness, might increase the potential compensation.
Common Causes Leading to Wrongful Death
Many situations can lead to a wrongful death claim. Some common causes include:
- Car Accidents: Often caused by drunk driving, distracted driving, or speeding. In Texas, for example, the number of fatal crashes involving distracted driving rose significantly in recent years, underscoring the devastating consequences of this behavior.
- Medical Malpractice: Surgical errors, misdiagnosis, and medication errors can all be grounds for a claim. Johns Hopkins researchers estimate that medical errors are a leading cause of death in the United States.
- Workplace Accidents: Construction accidents, exposure to hazardous materials, and inadequate safety measures are frequent culprits.
- Defective Products: Faulty car parts, dangerous medications, and unsafe consumer goods can lead to fatalities.
- Premises Liability: Deaths occurring due to unsafe conditions on someone else’s property, like slip-and-fall accidents or inadequate security.
Who Can File a Wrongful Death Claim? Standing to Sue
State laws dictate who has the legal right (“standing”) to file a wrongful death claim. Typically, this includes:
- Spouse: The surviving spouse is usually the primary claimant.
- Children: Biological and adopted children can typically file a claim.
- Parents: In some cases, parents can file a claim, especially if the deceased was a minor or financially supporting them.
- Other Dependents: Some states allow other dependents, like siblings or grandparents, to file a claim under specific circumstances.
The specific rules vary widely. For instance, in New York, the personal representative of the deceased’s estate typically brings the claim, acting on behalf of the eligible beneficiaries. In contrast, some states allow each eligible family member to file an individual claim.
Building a Strong Wrongful Death Claim: Evidence and Investigation
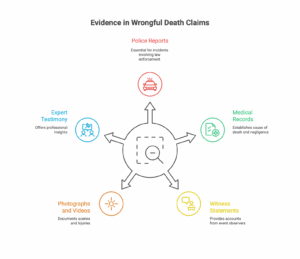
A strong wrongful death claim relies on solid evidence. This might include:
- Police Reports: Crucial for car accidents and other incidents involving law enforcement.
- Medical Records: To establish the cause of death and any medical negligence.
- Witness Statements: Accounts from people who witnessed the event.
- Photographs and Videos: Documentation of the scene, injuries, or defective products.
- Expert Testimony: Medical experts, accident reconstructionists, and other professionals can provide crucial insights.
Proving negligence is central to a successful wrongful death claim. This often involves demonstrating that the defendant had a duty of care, breached that duty, and that the breach directly caused the death. A thorough investigation is vital to uncover all relevant evidence.
Pursuing a Wrongful Death Claim: The Legal Process
Filing a wrongful death claim generally involves these steps:
- Consultation with an Attorney: An attorney can evaluate your case, explain your rights, and guide you through the legal process.
- Investigation: Gathering evidence and building a strong case.
- Filing a Complaint: Officially initiating the lawsuit in court.
- Discovery: Exchanging information with the opposing party through interrogatories, depositions, and document requests.
- Negotiation: Attempting to reach a settlement with the defendant.
- Trial: If a settlement cannot be reached, the case proceeds to trial.
A crucial aspect is the statute of limitations, which sets a deadline for filing a wrongful death claim. This deadline varies by state. For instance, many states have a two-year statute of limitations, while others may allow three years. Missing this deadline means losing the right to sue.
Seeking Justice and Compensation: Holding Negligent Parties Accountable in Wrongful Death Cases
A successful wrongful death claim can provide financial compensation to help families cope with their loss. This compensation may include:
- Lost Income: The income the deceased would have earned over their lifetime.
- Medical Expenses: Costs incurred for the deceased’s medical treatment before death.
- Funeral and Burial Expenses: Covering the costs of the funeral and burial.
- Loss of Companionship: Compensation for the emotional loss of the deceased’s love, support, and guidance.
- Pain and Suffering: In some states, compensation for the pain and suffering experienced by the deceased before death.
Defendants may raise defenses, arguing that they were not negligent, that their negligence did not cause the death, or that the deceased was partially at fault. An experienced attorney can anticipate and counter these defenses.
Beyond financial compensation, pursuing a wrongful death claim can also bring a sense of justice and closure to grieving families. It holds negligent parties accountable for their actions and can prevent similar tragedies from happening in the future.
Dealing with the loss of a loved one is incredibly difficult. Remember that resources are available to help you cope with the emotional toll. Support groups, grief counseling, and mental health professionals can provide valuable assistance during this challenging time.
If you believe a loved one died due to someone else’s negligence, seeking legal advice is essential. An attorney can assess your case, explain your options, and help you pursue justice and compensation.






